SPF, DKIM, DMARC Security Tool
Check your domain's email security configuration to ensure proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are in place.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
The 3 primary pieces of DNS-based email authentication are: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Each one is a DNS TXT record. Email recipients use the record values to verify that emails were authorized by the domain owner.
If these DNS records are configured incorrectly (or not configured at all) the receiving email server cannot verify the email. Many mail servers will not deliver unverified emails. While this is a good security measure, it will disrupt the senders business operations. In the worst case, the receiving mail server will still deliver the mail allowing attackers to spoof emails from the domain.
What is SPF?
The SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a DNS TXT record which lists the domains and IP addresses that are allowed to send emails on behalf of the domain. For example, it may a specific IP address such as 123.123.123.123 or the domain of an email provider such as amazonses.com.
What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an authentication mechanism that uses a cryptographic signature to sign and verify emails. The email sender generates a private and public key pair. The private key is used to sign the email and the public key is used to by recipients to verify received emails. The public key is published in the DNS TXT record.
Domain's can have multiple DKIM records. Each record is identified by a prefix called the DKIM selector. For example, if the selector is "mail" and the domain is "example.com", the DKIM record would be located at "mail._domainkey.example.com".
Different email providers use different default selectors. For example:
- Google Workspace typically uses "google"
- Microsoft 365 often uses "selector1" and "selector2"
- SendGrid uses "sendgrid"
- Mailgun uses "mailgun"
- Many providers use common patterns like "default", "s1", "k1", or "key1"
How to Find Your DKIM Selector
The most definitive way to find your DKIM selector is to check the email headers of an email sent from your domain. Every sent email includes the selector so that the recipient knows which DNS record to use for DKIM verification.
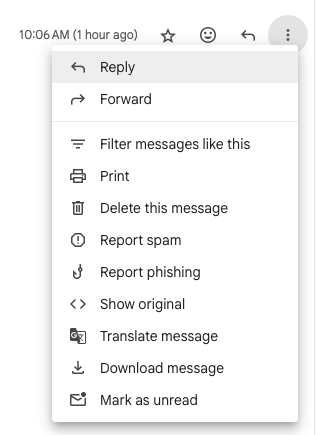
To check the email headers, follow these steps:
- Send a test email from your domain
- Open the email and view the original/source message. For example in Gmail, click the three dots to open the full email actions menu and then click "Show original"
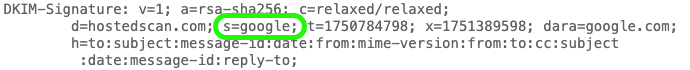
- Look for the "DKIM-Signature" line
- Find "s=" - the value after it is your selector (e.g., s=mail1)
What is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is protocol which builds on top of SPF and DKIM. A domain's DNS record for DMARC contains instructions for how email recipients should handle emails which fail security verification and where they should report these failures. For example, it may instruct the recipient to reject failing emails and to report the failures to mailto:dmarc@example.com.
Ready for the next step?
HostedScan is a best-in-class solution for attack surface management and vulnerability scanning